The cloud networking architecture specifies how information moves between physical infrastructure, virtualized networks, and applications and services. The article discusses everything about cloud networking architecture.
The foundation of cloud computing is cloud networking architecture, which enables businesses to take advantage of virtualization, scalability, and global reach. Hence, it is a dynamic, developing field that nevertheless plays a crucial part in contemporary IT infrastructure.
Modern IT infrastructure must include cloud networking architecture for businesses to scale and improve performance. Hence, it strengthens security to keep your documents safe. However, cloud networking architecture frequently includes real-time monitoring, analytics, and management tools and services. Read below to learn about cloud networking architecture.
See Also: The Future Is Now: Exploring the Intersection of Web Design and Software
10 Building Blocks Of Cloud Networking Architecture
Cloud networking architecture involves a collection of components to form a solid and dependable network infrastructure. Below are the building blocks of cloud networking architecture.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
A VPC, which offers a logically isolated network within a cloud service provider’s infrastructure, is the cornerstone of cloud networking architecture. Hence, it gives you control over network settings by allowing you to build your IP address ranges.

By isolating resources into several subnets or availability zones, VPCs make network segmentation possible, assisting enterprises in maintaining security and compliance.
Subnetting
Subnetting is the process of breaking up the IP address range of a VPC into smaller, easier-to-manage chunks. However, it enables greater routing control, security, and resource organization within the VPC. Depending on the use case, subnets can be public (available from the Internet) or private (separated from the Internet).
Load Balancers
Load balancers split incoming traffic among many resources or instances to guarantee high availability. By routing requests to healthy samples and removing overloads, they play a crucial role in maximizing application performance.
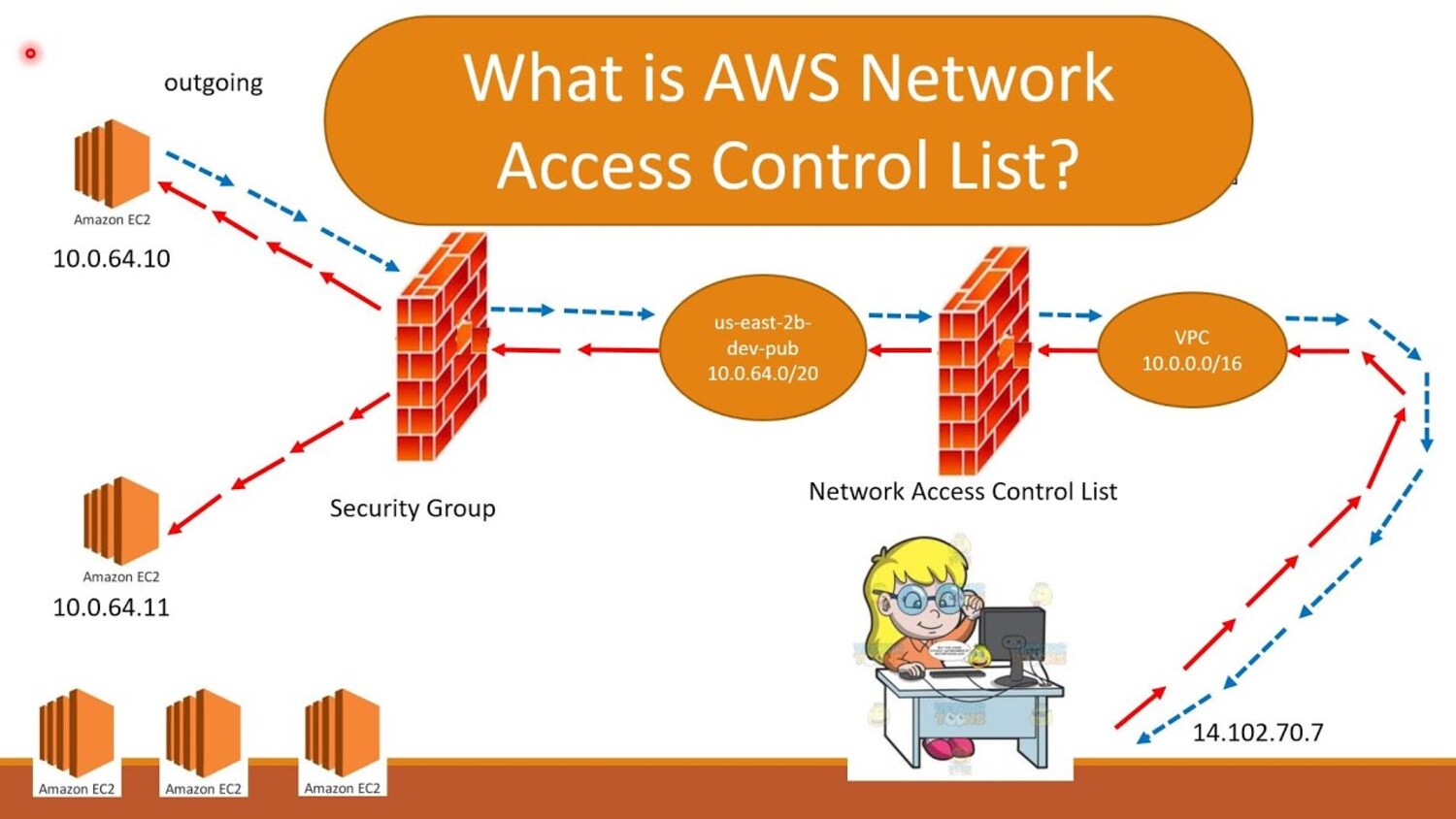
NACLs And Security Groups
Security Groups and NACLs are crucial for regulating traffic entering and leaving a VPC’s resources. While NACLs function at the subnet level, Security Groups operate at the instance level, giving users more precise control over network traffic.
Direct Connect And Virtual Private Network (VPN)
VPNs and Direct Connect provide secure connections between on-premises data centers and the cloud. While Direct Connect offers dedicated, private connections for improved reliability and lower latency, VPNs use encrypted tunnels over the open Internet.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
By caching and serving material from edge sites close to end users, CDNs increase the performance and availability of online applications.
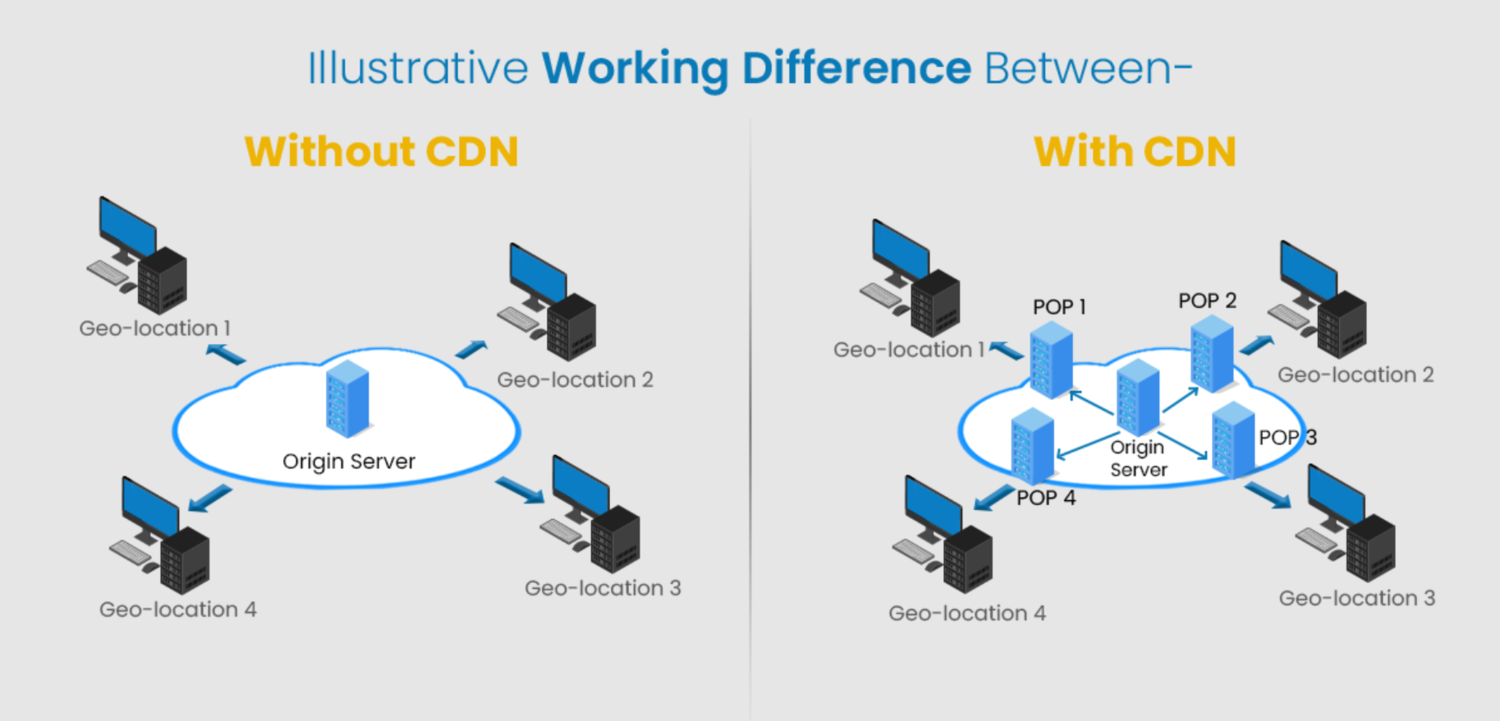
However, they improve user experience by lowering latency and lightening the strain on origin servers.
Transit Gateway
By serving as a hub for linking several VPCs, on-premises data centers, and external networks, Transit Gateway streamlines network design. Hence, it centralizes network management, streamlines routing, and simplifies things.
Route Tables And Route Propagation
The routing paths within a VPC are defined by route tables, which guide traffic to the proper locations. Route propagation also allows updating routes dynamically between VPN connections or VPCs, guaranteeing effective network connectivity.
Monitoring And Logging
Continuous logging and monitoring are needed for cloud networking architecture to identify and address network problems and security concerns. Hence, services provide real-time visibility into network performance and security.
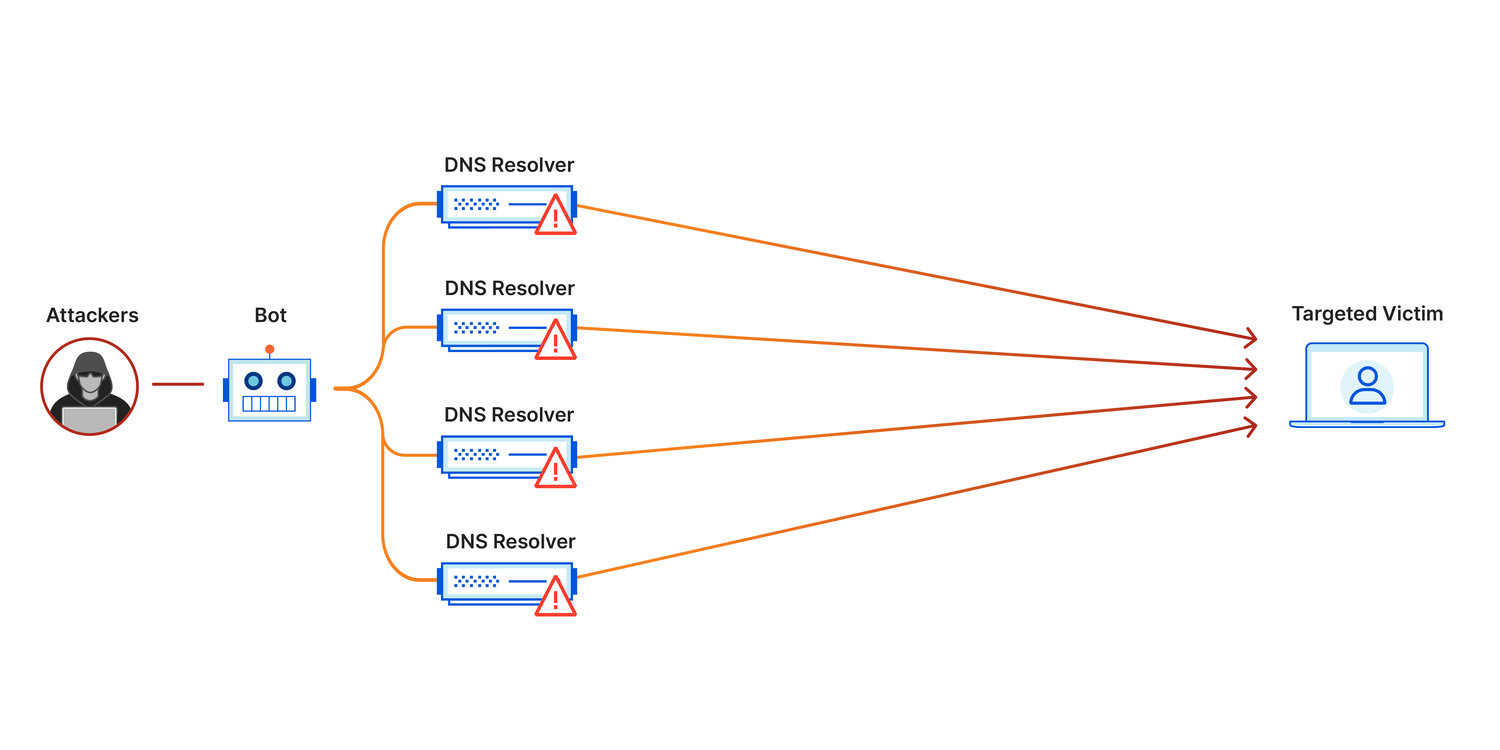
Network Security Services
The security of cloud networks is improved by cutting-edge security services, including Web Application Firewalls (WAF), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) defense, and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS). These services also aid in defending software and data from online threats and unlawful access.
Cloud Networking Architecture Deployment Methods
When creating and administering their infrastructure in the cloud, enterprises must use specific cloud networking architecture deployment methods. Here are the three primary cloud networking architecture deployment methods.
Read also: Set Up Bluestacks Cloud Connect With Step-By-Step Tutorial
Traditional On-Premises Extension
This deployment technique replicates a minimally modified version of an organization’s current on-premises infrastructure in the cloud. This method involves migrating virtual machines, databases, and applications to the cloud without significant architectural modifications. This approach is frequently employed by companies that wish to swiftly migrate their workloads to the cloud to benefit from scalability and cost-effectiveness without redesigning their applications completely.
Its familiarity is one of its main benefits. IT professionals may simplify the conversion process using their current knowledge and configurations. Hence, this approach is appropriate for legacy systems or those that are difficult to rework for cloud-native settings.
It may only partially reap the advantages of the cloud. Although it offers fundamental scalability and availability enhancements, it does not fully utilize cloud-native features like serverless computing or demand-based auto-scaling. Additionally, since firms can still operate resources continuously rather than taking advantage of pay-as-you-go pricing, it might not optimize expenses as effectively as alternative approaches.
Cloud-Native Architecture
A “cloud-native architecture” technique involves designing infrastructure and applications exclusively for the cloud. Organizations rebuild or redesign their applications to use cloud services like serverless computing, managed databases, and microservices rather than simply moving their current systems.
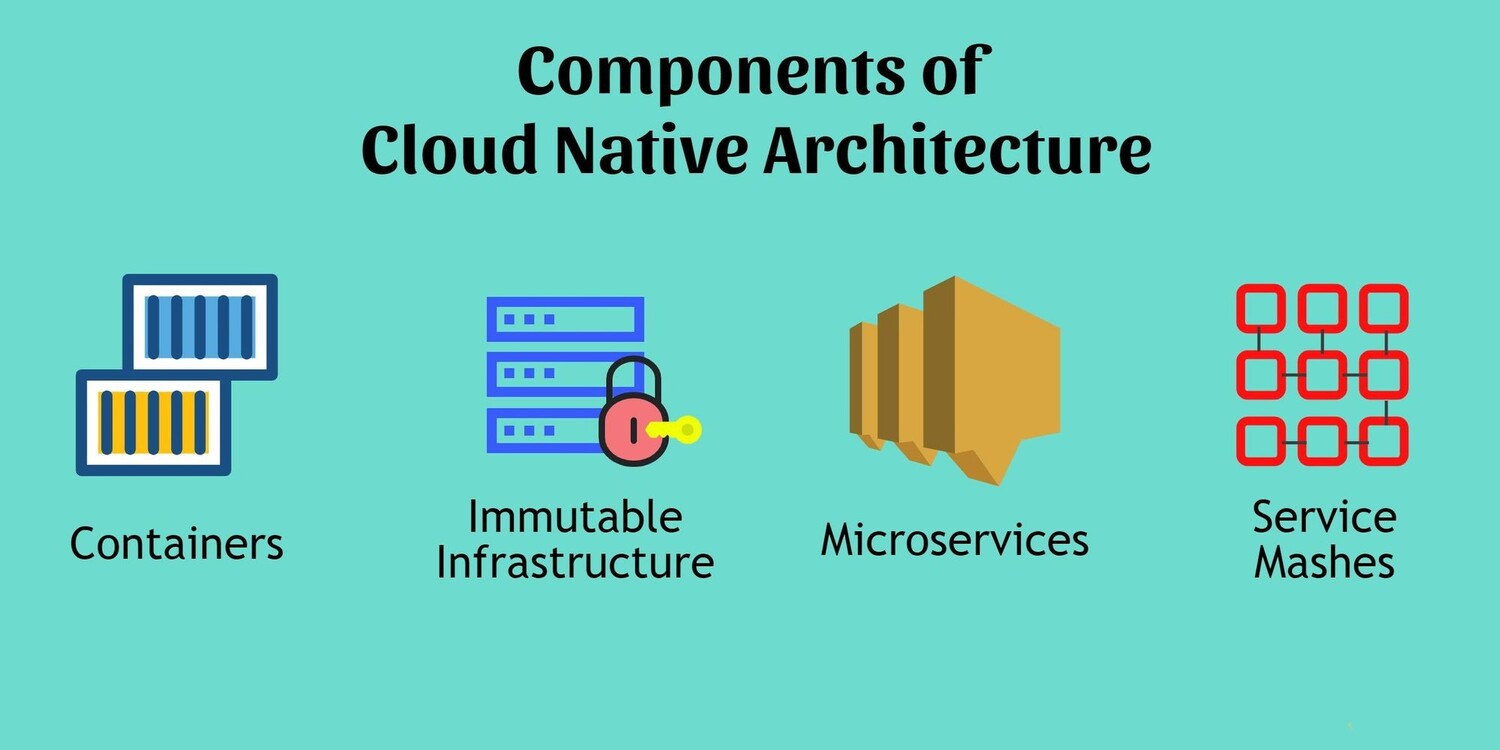
However, cloud networking architecture makes the most of cloud advantages like cost reduction and auto-scaling while allowing developers to concentrate on developing code rather than maintaining infrastructure. Microservices also improve agility by enabling application components’ autonomous development and scaling.
However, implementing a cloud-native strategy necessitates a substantial change in perspective and procedures.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud deployment enables businesses to connect their current data centers and cloud environments. Hence, this strategy is appropriate for companies with on-premises workload requirements or regulatory restrictions.
However, this technique makes it possible to migrate data and workloads seamlessly, guaranteeing consistent operations in both environments. While hybrid clouds offer flexibility, they can also be more challenging to maintain regarding cloud networking architecture security and data synchronization.
How Do You Pick A Cloud Network Architecture?
Your immediate and long-term requirements heavily influence your final decision on a cloud networking architecture. The built-in tools or third-party virtual network alternatives are available to businesses looking to implement a hybrid architecture with a single primary provider. Also, a multi-cloud management platform might suit people with highly scattered multi-cloud objectives.
Another point is whether SaaS or IaaS will ultimately be the organization’s long-term plan.
FAQs
What benefits does cloud networking offer?
Scalability, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and accessibility are benefits of cloud networking. Cloud networks make it possible for resources to be scaled easily, capital costs to be decreased, demands to be changed quickly, and the world to be accessible. Hence, they are perfect for modern enterprises and IT infrastructure.
Why do we need cloud networking?
Cloud networking is required to offer practical and adaptable access to computing resources, data storage, and services over the Internet. It enables enterprises to react to changing demands, improve agility, and concentrate on core business operations. However, it also offers scalability, cost savings, global accessibility, and enhanced security.
What is the architecture of the cloud network?
The design and organization of the interconnected parts that make up a cloud computing environment is known as cloud network architecture. Subnets, load balancers, security groups, routing tables, and various cloud services are frequently included with virtual private clouds (VPCs).
What in cloud computing is SLA?
An outsourcing and technology vendor contract, known as a service level agreement (SLA), specifies the degree of service a supplier agrees to provide to the customer. Metrics include uptime, delivery, reaction, and resolution time.
Conclusion
It was all about the cloud networking architecture. In conclusion, cloud networking ensures that businesses benefit from the power of the cloud while still having control over their network resources. However, a well-optimized, secure cloud network that satisfies the requirements of today’s digital ecosystem requires careful planning and configuration of these building parts.
See also: How to setup VPN in Mikrotik Router for Remote Access
He is a Tech Geek, Gadget Expert, SEO Expert, Web Designer, and a Blogger. Having a technology background gives him a unique perspective!
